

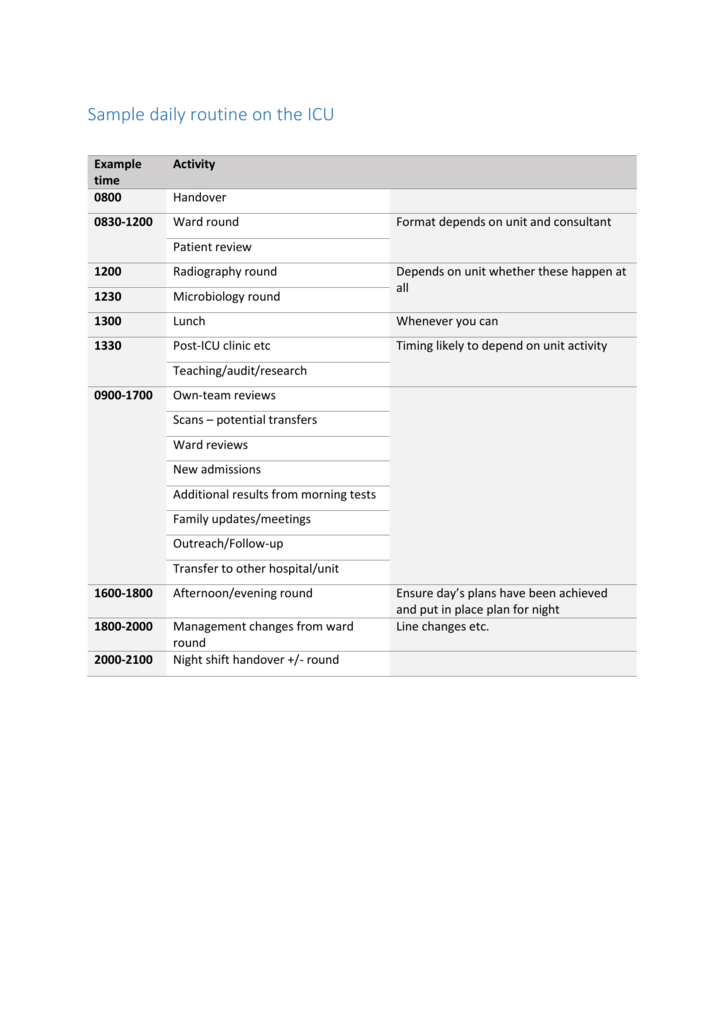
Common conditions cared for include prematurity and associated complications, congenital disorders such as congenital diaphragmatic hernia, or complications resulting from the birthing process. In the European model, mobile ICU teams are usually led by a nurse and physician.Ĭares for neonatal patients who have not left the hospital after birth. In the Anglo-American model of pre-hospitalisation care mobile ICUs are generally crewed by specialised advanced life support paramedics. Mobile ICUs are generally used for people who are being transferred from hospitals and from home to a hospital. Īn intensive care unit for patients with suspected or diagnosed contagious diseases that require medical isolation.Ī specialized ambulance with the team and equipment to provide on-scene advanced life support and intensive care during transportation. It may also be called an intermediate care area, step-down unit, or progressive care unit. It is utilised until a patient's condition stabilizes to qualify for discharge to a general ward or recovery unit. Some large hospital trauma centers, especially but not exclusively in the United States, divide their main ICU, and perhaps even the other ICUs they may have, into sections that cater to those needing regular intensive care (the regular ICU), and those who are extremely unstable or near death, needing an even higher level of care (the critical care unit, or section).Ī special intensive care unit dedicated to management of critically ill elderly.Īn intermediate ward for patients who require close observation, treatment and nursing care that cannot be provided in a general ward, but whose care is not at a critical stage to warrant an ICU bed. Hospitals may have various specialized ICUs that cater to a specific medical requirement or patient:Ĭaters to patients specifically with life-threatening cardiac conditions such as a myocardial infarction or a cardiac arrest. This led to the routine use of cardiac monitoring in ICUs, especially after heart attacks. In the 1960s, the importance of cardiac arrhythmias as a source of morbidity and mortality in myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) was recognized.
The first application of this idea in the United States was in 1955 by William Mosenthal, a surgeon at the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center. In response to a polio epidemic (where many patients required constant ventilation and surveillance), Bjørn Aage Ibsen established the first intensive care unit globally in Copenhagen in 1953. Safar is considered to be the first practitioner of intensive care medicine as a speciality.

In 1950, anesthesiologist Peter Safar established the concept of advanced life support, keeping patients sedated and ventilated in an intensive care environment. Although this was not the case, her experiences during the war formed the foundation for her later discovery of the importance of sanitary conditions in hospitals, a critical component of intensive care. Until recently, it was reported that Nightingale’s method reduced mortality from 40% to 2% on the battlefield. In 1854, Florence Nightingale left for the Crimean War, where triage was used to separate seriously wounded soldiers from those with non-life-threatening conditions. Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications. Common conditions that are treated within ICUs include respiratory and cardiovascular, as well as neurology. ICUs are also distinguished from general hospital wards by a higher staff-to-patient ratio and access to advanced medical resources and equipment that is not routinely available elsewhere. They are staffed by highly trained physicians, nurses and respiratory therapists who specialize in caring for critically ill patients. Intensive care units cater to patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses and injuries, which require constant care, close supervision from life support equipment and medication in order to ensure normal bodily functions. ICU patients often require mechanical ventilation if they have lost the ability to breathe normally.Īn intensive care unit ( ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit ( ITU) or critical care unit ( CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
